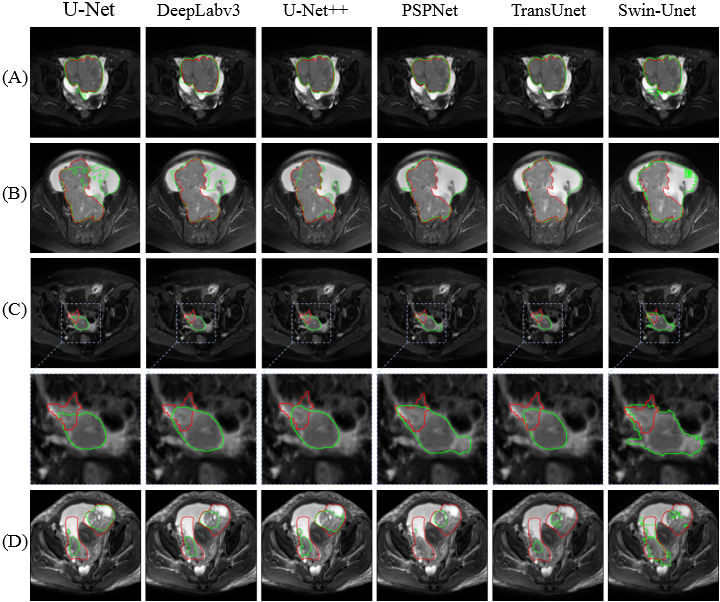
Visual comparison of segmentation results of different models. Image Credit: SIBET
Around 90-95% of all ovarian cancers are epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). The standard treatment strategy for EOC comprises surgical tumor debulking and administration of intravenous chemotherapy.
Scientists, headed by Xin Gao at the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, employed deep learning in EOC segmentation and assessed its feasibility.
Tumor assessment before surgery is of paramount importance to guide treatment decisions and can ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Xin Gao, Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Finding and depicting the tumor area (EOC segmentation) is a prerequisite for tumor assessment, which also streamlines following efficacy evaluation.
But EOC segmentation is normally executed slice by slice in clinical practice, which is both laborious and burdensome. Hence, a solution to this issue is required immediately.
With the rapid growth of medical image data, the need for fully automated EOC segmentation methods is becoming more and more urgent.
Dingdu Hu, Study First Author, Chinese Academy of Sciences
A total of 339 magnetic resonance images of EOC patients from eight hospitals in their study were utilized by GAO and his group. Around five evaluation metrics were chosen to evaluate the segmentation performance of various models.
Their outcomes displayed that U-Net++ obtained optimal segmentation results in both internal and external test sets illustrating the excellent precision and generalization of the model.
Besides, the team additionally examined the effects of tumor stage and histological type on the models’ segmentation performance.
But the segmentation precision of the model for advanced-stage tumors and serous tumors is comparatively low, “indicating that different tumor stages and histological types have an influence on the segmentation performance of the model,” said GAO.
This study explores and confirms the possible application of artificial intelligence methods for the completely automated segmentation of EOC.
When combined with the team’s earlier studies on the differentiation of epithelial ovarian tumors and type I and II EOC, an end-to-end, completely automated EOC diagnostic process has a great possibility for enhancing clinical efficiency.
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Journal Reference
Hu, D., et al. (2023) Deep learning-based segmentation of epithelial ovarian cancer on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. doi.org/10.21037/qims-22-494.