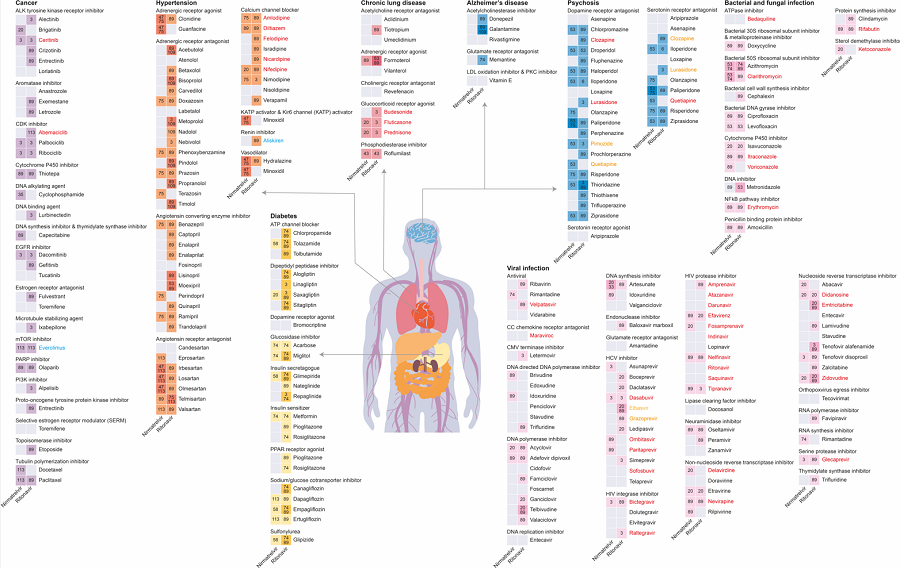
Results of drug interaction prediction between Paxlovid ingredients and representative approved drugs using DeepDDI2. Image Credit: Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology.
The research was conducted by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research group in the Department of Biochemical Engineering, which examined the interaction between the PaxlovidTM ingredients that are utilized as a COVID-19 treatment as well as in other prescription drugs.
This study was reported in the online edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of America (PNAS), an internationally renowned academic journal, on March 13th, 2023.
The research group came up with DeepDDI2, an advanced version of DeepDDI, an AI-based drug interaction prediction model that was developed in 2018. DeepDDI2 has the potential to compute and process 113 drug-drug interaction (DDI) types over the 86 DDI types that have been covered by the present DeepDDI.
DeepDDI2 was utilized by the research group to predict possible interactions between the ingredients (nirmatrelvir, ritonavir) of Paxlovid*, a COVID-19 treatment, as well as other prescription drugs.
The research group made use of DeepDDI2 to forecast how Paxrovid’s components, nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, would interact with 2,248 prescription drugs. After the predictions, ritonavir was anticipated to interact with 1,403 prescription drugs and nirmatrelvir with 673 drugs.
With the help of the prediction outcomes, the research group suggested alternative drugs with a similar mechanism but low drug interaction ability for prescription drugs consisting of high adverse drug events (ADEs).
Consequently, 124 alternative drugs are available that could help decrease the possible adverse DDI with ritonavir, and 239 alternative drugs for nirmatrelvir were determined.
With this research achievement, it was possible to use deep learning technology to precisely forecast drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and this is anticipated to play a significant role in the precision medicine, digital healthcare, and pharmaceutical industries by offering valuable data in the process of coming up with new drugs and making prescriptions.
The results of this study are meaningful at times like when we would have to resort to using drugs that are developed in a hurry in the face of an urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, that it is now possible to identify and take necessary actions against adverse drug reactions caused by drug-drug interactions very quickly.
Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
This study was performed with the assistance of the KAIST New-Deal Project for COVID-19 Science and Technology and the Bio·Medical Technology Development Project aided by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Journal Reference
Kim, Y., et al. (2023) Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2221857120.