May 13 2014
Plasma technology based on Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) has been widely demonstrated to be a novel active flow control method.
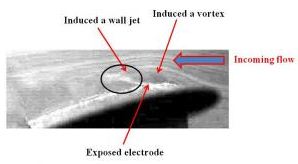 This shows the flow field around the plasma actuator. Credit: ©Science China Press
This shows the flow field around the plasma actuator. Credit: ©Science China Press
In order to make the plasma flow control technology more practical, the plasma authority must be improved at high wind speed. Dr. ZHANG Xin and his group from School of Aeronautic, Northwestern Polytechnical University set out to tackle this problem. After 2-years of innovative research, they have developed a novel plasma actuator to improve the plasma authority at high wind speed. They found that the novel plasma actuator acting on the surface of UAV could obviously suppress the boundary layer separation and reduce the model vibration at the wind speed of 100 m/s. Their study expanded the plasma actuator authority and demonstrated an important role of plasma actuator in the real application. Their work, entitled "Unmanned air vehicle flow separation control using dielectric barrier discharge plasma at high wind speed", was published in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. 2014, Vol 57(6).
Plasma flow control technology based on DBD has been widely demonstrated to be a novel active flow control method for boundary layer control, lift augmentation and separation control. Compared with the traditional active flow control, the plasma flow control has simple structure without moving parts and is convenient for real time control due to its fast response. Many researchers have engaged in the study of plasma flow control. However, in the existing literature, the wind speeds of stall separation control on three-dimensional aerial vehicle using DBD plasma actuator so far were no more than 50 m/s, but the flow speed of real flight is generally above 100 m/s. Therefore, in order to make the plasma flow control technology more practical, the plasma authority must be improved at higher wind speeds.
This work explored the aerodynamic control using novel plasma on a UAV at high wind speeds. The results indicated that the novel plasma actuator was not only jet actuator but also vortex generator, as shown in Figure 1. It can create relatively large-scale disturbances in the separated wake shear layer and promote momentum exchange between low speed and high speed regions which lead to shear layer separation delay. It was found that the maximum lift coefficient of the UAV was increased by 2.5% and the lift/drag ratio was increased by about 80% at the wind speed of 100 m/s. This study demonstrated an important role of plasma actuator in the real application.