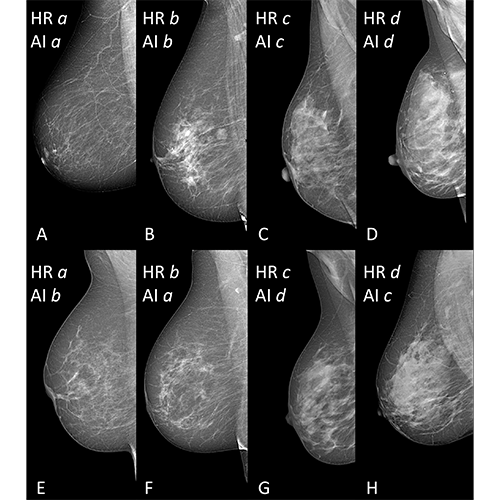
Image Credit: Magni et al, Radiology: Artificial Intelligence; @RSNA 2022.
The quantity of fibroglandular tissue in the breast that may be observed on mammograms is referred to as breast density. High breast density is a significant risk factor for breast cancer, and it lowers mammography sensitivity by disguising underlying lesions. As a result, many states in the United States have legislation requiring women with thick breasts to be advised after a mammogram so that they can opt for additional tests to enhance diagnosis of cancer.
Breast density is visually measured on two-view mammograms in clinical practise, most typically using the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) four-category scale, which ranges from nearly completely fatty breasts to highly dense breasts. Visual classification is subject to inter- and intra-observer variability, hence the approach has limitations.
Researchers in Italy developed software for breast density categorization based on deep learning with convolutional neural networks, a powerful type of AI capable of detecting small patterns in images beyond the capability of the naked eye, to combat this variability. The software, known as TRACE4BDensity, was taught by the researchers under the guidance of seven qualified radiologists who individually examined 760 mammographic pictures.
On a dataset of 384 mammographic pictures obtained from a separate centre, the tool was externally validated by the three radiologists who were closest to the consensus.
Density Assessment Aids Risk Stratification and Decision Making
TRACE4BDensity was able to identify between low density (BI-RADS categories A and B) and high density (BI-RADS categories C and D) breast tissue with an accuracy of 89%, with a 90% agreement between the tool and the three readers. All of the conflicts were in the same BI-RADS category.
The particular value of this tool is the possibility to overcome the suboptimal reproducibility of visual human density classification that limits its practical usability. To have a robust tool that proposes the density assignment in a standardized fashion may help a lot in decision making.
Sergio Papa, MD, Study Co-Author, Centro Diagnostico Italiano
The researchers believe that such a tool might be especially useful as breast cancer screening gets more individualized, with density assessment being one major aspect in risk categorization.
“A tool such as TRACE4BDensity can help us advise women with dense breasts to have, after a negative mammogram, supplemental screening with ultrasound, MRI or contrast-enhanced mammography,” said another study co-author Francesco Sardanelli, MD, from the Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico Policlinico San Donato in San Donato, Italy.
Additional experiments are being planned by the researchers to better comprehend the software’s complete potential.
Study co-author Christian Salvatore, PhD, senior researcher, Scuola Universitaria Superiore Pavia, and co-founder and chief executive officer of DeepTrace Technologies comments, “We would like to further assess the AI tool TRACE4BDensity, particularly in countries where regulations on women density is not active, by evaluating the usefulness of such tool for radiologists and patients.”
Journal Reference:
Magni, V., et al. (2022) Development and Validation of an AI-driven Mammographic Breast Density Classification Tool Based on Radiologist Consensus. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. doi.org/10.1148/ryai.210199.